Tannaz Mostafid

Here is a summary of my projects, including my master's thesis and recent ML and DL projects.
Selected Projects:
YOLO11n-Deep Learning for X-ray Bone Fracture Detection
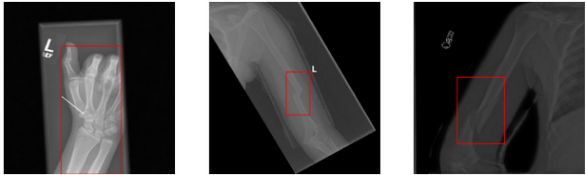
Figure 1: Studied Segmentation Network,Created by autor.
Summary:
This is ongoing project aims to develop and validate deep learning models for detecting bone fractures in medical X-ray images using object detection methods. It involves training convolutional neural networks to accurately detect and classify fractures, ensuring high diagnostic accuracy. In addition, a web application was created using FastAPI and Streamlit, and containerised using Docker for efficient and reliable deployment.
Exploring CNN Components for Tumor Segmentation in MRI Images:An Ablation Study
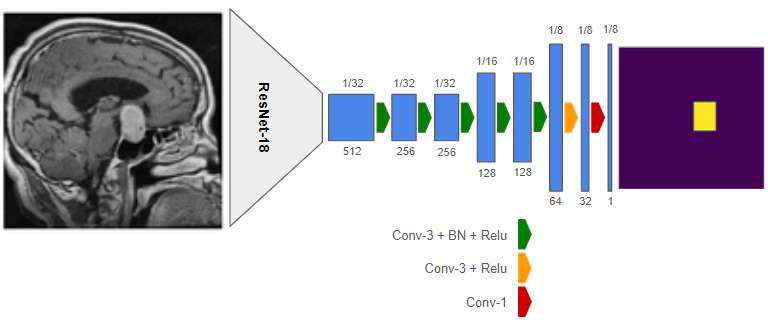
Figure 2: Studied Segmentation Network,Created by autor.
Summary:
In this project, I explore the impacts of different components of an encoder-decoder convolutional neural network (CNN) for tumor segmentation in the 2D MRI Brain Tumor Image Dataset.
I propose the CNN model shown in Figure 1 and compare the performance of ResNet-18 and VGG-16 backbones. The influence of elastic data augmentation techniques is examined, followed by an exploration of various modifications in the decoder architecture, including different upsampling levels, skip connections, and dilated(atrous)convolutions. I also compare the effectiveness of Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) and Dice loss functions in training the model.
Experimental results indicate that, for this dataset, ResNet-18 is a better choice for the backbone, and BCE results in slightly better training performance. Additionally, using dilated convolutions in the decoder improves segmentation results. Moreover, augmentation helps increase the model’s generalizability.
Methods:
I conducted oblation studies, to assess the effects of network structure on segmentation results,on different parts of my base network (see Figure 1). All experiments were performed on Google Colab with GPU acceleration, and the learning rate was adjusted based on the learning curve of each experiment.
Deep Learning(PyTorch),Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Computer Vision (OpenCV & pretrained CNNs), Image Semantic Segmentation(ResNet-18, VGG-16), Data Augmentation(Elastic, Affine),Loss Functions(BCE,DiceLoss)
Final Experiment:
In the final experiment, I incorporated the findings from the previous ablation studies. I used the baseline model with dilated convolutions as explained earlier, applied the BCE loss function, and randomly applied augmentation to 50% of the samples. Table 1 shows the segmentation results on the validation and test sets. Compared to Table 4, the test results show a significant improvement over the previous experiments.
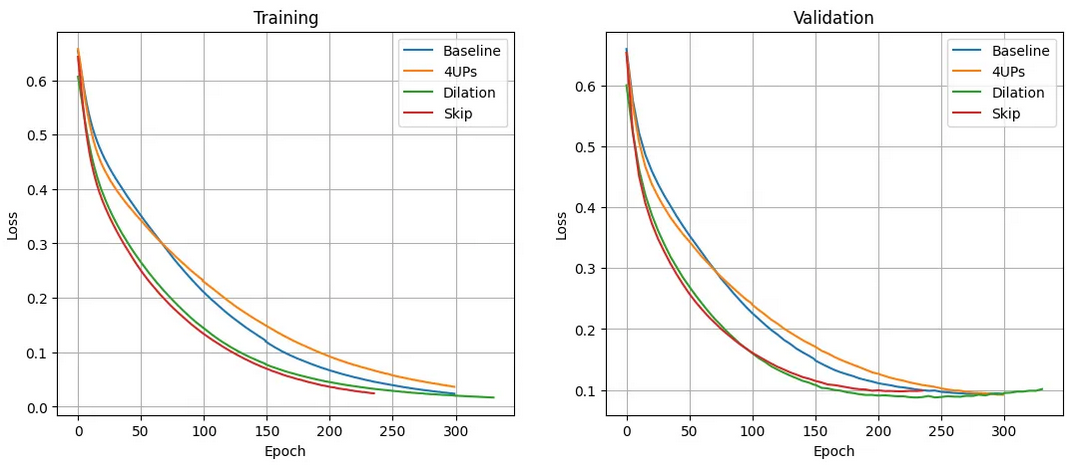
Figure 2 : Training and validation curves for different decoder structures. Created by author Created by author
In ResNet the goal is to preserve the input(idebntiy) through the skip connections , and add the input to the output of series of layers . so NN learn the residuals instead of entire mapping

Table 1: Segmentation results for the final model and experiment setup on the validation and test sets. All training samples were used for this experiment. Created by author..
GitHub repo:
Articles out of this project:
Exploring CNN Components for Tumor segmentation in MRI Images:An oblation study
Tumor Semantic Segmentation with U-Net and Deeplabv3+
##
Comparative Analysis of CNN Architectures for Brain Tumor Classification in MRI Images
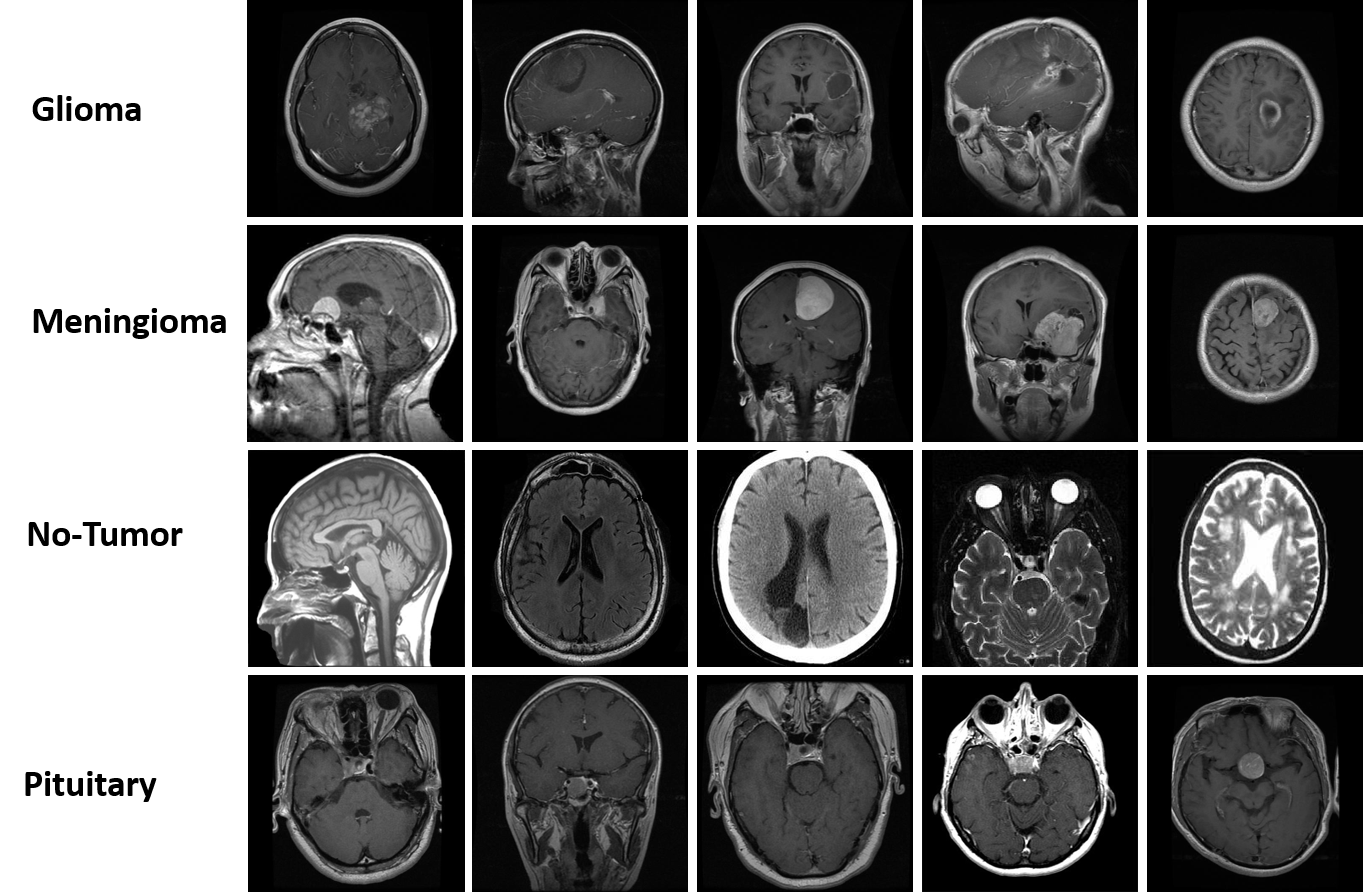
Figure 2:Sample images from the Brain Tumor Classification dataset.Photo created by autor
Summary:
This project aims to evaluate the performance of four leading deep convolutional neural network(CNN) models, including VGG16, ResNet50, Xception, and MobileNet in classifying brain tumors.The implementations are based on TensorFlow and Keras, using the Categorical Cross-Entropy loss and the Adam optimizer. Data augmentation is applied during model training to increase diversity and generalizability. Experiments are performed on Google Colab.
Methods:
I evaluated the performance of VGG16, ResNet50, Xception, and MobileNetV1 for brain tumor classification using MRI images. The dataset was split into 2870 training and 394 test images, with a validation set from 15% of the training set. Data augmentation (rotation, flipping, zooming, etc.) and normalization (rescale to [0, 1]) were applied.
Experiments were conducted on Google Colab with GPU acceleration. Pre-trained models were fine-tuned on the last three layers. I used the Adam optimizer and Categorical Cross-Entropy loss, adjusting learning rates and epochs to prevent overfitting.
Model performance was evaluated using confusion matrices, precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy metrics.
Evaluation
Here I provides a quantitative evaluation of the trained models on the test set, including Precision, Recall, F1-Score, Accuracy, and class-size weighted Accuracy metrics. The best value for each metric is highlighted in green. wACC indicate the class-size weighted accuracies.
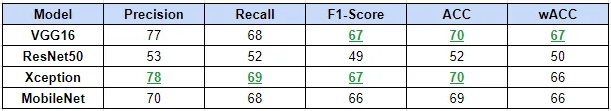
Table 2: Model evaluation on the test set,Created by autor.
GitHub repo:
Articles out of this project:
Overview of VGG16, ResNet50, Xception and MobileNet Neural Networks
##
NLP Sentiment Analysis
Summary
In this project, I investigate Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques for sentiment analysis using Python and libraries such as NLTK, Spacy, and Hugging Face. I implement four text preprocessing combinations, including basic preprocessing, stemming, and part of speech (POS) tagging, followed by bag-of-words vectorization. Word vocabularies are evaluated using frequency distributions and word entropies, demonstrating that relying solely on word frequencies is insufficient for vocabulary generation. Additionally, I recognize the importance of exploring TF-IDF and addressing data imbalances to enhance sentiment representation and modeling.
Methods
I conducted experiments using four text preprocessing combinations: basic preprocessing, stemming, POS tagging, and bag-of-words vectorization. Evaluations of word vocabularies were performed using frequency distributions and word entropies. The experiments highlighted the limitations of relying solely on word frequencies for vocabulary generation. To improve sentiment analysis, I identified the need to explore TF-IDF and address data imbalances. All experiments were carried out using Python with libraries including NLTK, Spacy, and Hugging Face.
Article out of this project:
##
fMRI Image Analysis and EEG Signal Processing
Summary:
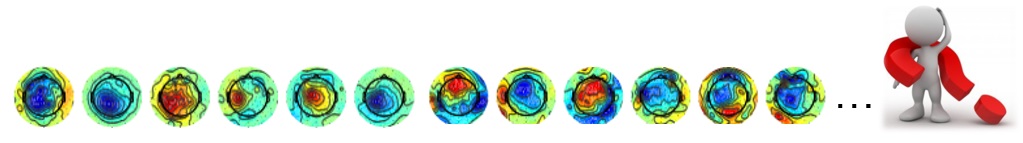
In my master’s thesis, I investigated the functional and anatomical variability of the hand knob on surface EEG through a two-part study.I conducted an extensive analysis of a large brain dataset comprising EEG and fMRI data using MATLAB. My research focused on feature extraction and pattern recognition. I investigated the impact of fMRI image variability on EEG, developing a cortical EEG pattern model.
Additionally, I proposed two criteria for selecting Common Spatial Pattern (CSP) filters to improve motor imagery neurofeedback applications for Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) research. My preliminary findings indicated that while the similarity of CSP filters to simulated anatomical patterns can be used to measure their plausibility, Event-Related Distribution may not always be an accurate measure. The results of my analysis were presented in my Master’s Thesis.
Methods:
The dataset consisted of separately recorded EEG and fMRI data from healthy subjects during hand motor activity. The hypothesis was that anatomical variability might correlate with cortical activity. To test this, I classified subjects into five categories based on the shape of their hand knob area and used the BrainStorm toolbox to simulate their cortical activity.
Due to the lack of simultaneous EEG and fMRI recordings, I marked motor activity on the structure based on fMRI data and simulated surface EEG using the BrainStorm toolbox for the selected area. I calculated Common Spatial Patterns (CSPs) from the EEG data and assessed their plausibility using a heuristic approach from the literature. To validate the hypothesis, I compared the simulated EEG patterns with CSPs based on their correlation and Event-Related Distributions (ERDs).
The results indicated that simulated EEG aids in selecting more plausible CSP filters, with correlation proving to be a better measure of similarity than ERD. Despite the limited number of subjects posing a challenge, the study demonstrated the value of using simulated EEG for improving CSP filter selection for motor imagery neurofeedback applications. Data preprocessing included segmenting EEG data into epochs, applying filtering, artifact removal, baseline correction, computing covariance matrices, spatial filter calculation, normalization, and classification.
View Results Presentation
View Publication on Medium
##